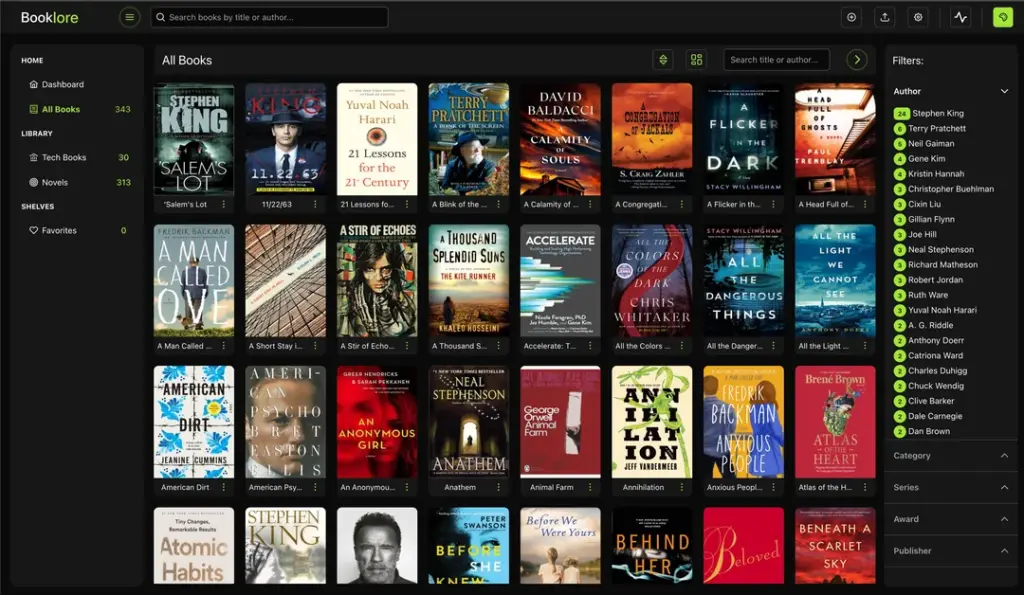
BookLore is a powerful, self-hosted application that transforms how you manage and read your digital book collection. By organizing PDFs and EPUBs in one centralized interface, it lets you access your entire library from any device with a browser—no proprietary platforms required. Docker Compose simplifies deployment by containerizing the application and its dependencies (like MariaDB), ensuring consistent performance across environments. Here’s how to set it up on Ubuntu.
Prerequisites
Before installing, ensure you have:
- Ubuntu 18.04 or later
- A user account with
sudoprivileges - Basic terminal familiarity
Step 1: Install Docker Engine
Docker is the foundation for running containers. Execute these commands:
# Update repositories
sudo apt update
# Install dependencies
sudo apt install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
# Add Docker’s GPG key
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
# Add Docker’s repository
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
# Install Docker
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
# Enable Docker at startup
sudo systemctl enable docker && sudo systemctl start docker
# Verify installation
sudo docker run hello-world You should see a confirmation message. If you encounter Permission denied errors, add your user to the docker group with sudo usermod -aG docker $USER, then log out and back in.
Step 2: Install Docker Compose
Docker Compose manages multi-container applications. Install the standalone version:
# Download the binary
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/latest/download/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
# Apply executable permissions
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
# Verify installation
docker-compose --versionTroubleshooting:
If you see docker-compose: command not found, create a symbolic link: sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/docker-compose /usr/bin/docker-composeStep 3: Deploy BookLore with Docker Compose
Create a directory for BookLore and navigate into it:
mkdir ~/booklore && cd ~/bookloreCreate a docker-compose.yml file:
nano docker-compose.ymlPaste this configuration, replacing /your/local/path/... with your actual directories:
services:
booklore:
image: ghcr.io/adityachandelgit/booklore-app:latest
container_name: booklore
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- TZ=Etc/UTC
- DATABASE_URL=jdbc:mariadb://mariadb:3306/booklore
- DATABASE_USERNAME=booklore
- DATABASE_PASSWORD=your_secure_password # Change this!
- SWAGGER_ENABLED=false
depends_on:
mariadb:
condition: service_healthy
ports:
- "6060:6060"
volumes:
- ./booklore/data:/app/data
- ./booklore/books:/books
restart: unless-stopped
mariadb:
image: lscr.io/linuxserver/mariadb:11.4.5
container_name: mariadb
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- TZ=Etc/UTC
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=super_secure_password # Change this!
- MYSQL_DATABASE=booklore
- MYSQL_USER=booklore
- MYSQL_PASSWORD=your_secure_password # Must match DATABASE_PASSWORD above
volumes:
- ./mariadb/config:/config
restart: unless-stopped
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "mariadb-admin", "ping", "-h", "localhost"]
interval: 5s
timeout: 5s
retries: 10Key adjustments:
- Replace
your_secure_passwordandsuper_secure_passwordwith strong passwords. - Use relative paths (e.g.,
./booklore/books) to avoid permission issues.
Launch the containers:
docker-compose up -dStep 4: Access and Use BookLore
Once running:
- Access the web UI at
http://your-server-ip:6060. - Upload books by placing files in
./booklore/books. - Browse your library, track reading progress, or use metadata tools.
Common Issues & Fixes
- Container name conflict:
- Error:
Cannot create container... name already in use. - Solution: Run
docker-compose downfirst, or delete conflicting containers withdocker rm -f container_name.
- Error:
- Slow file access on macOS/Windows:
- Docker’s VM layer slows volume mounts. Use Docker volumes instead of host paths if performance suffers.
- Dependency boot failures:
- MariaDB might not initialize before BookLore starts. The
condition: service_healthydirective in the config prevents this.
- MariaDB might not initialize before BookLore starts. The
- Permission errors:
- Ensure your local paths (e.g.,
./booklore/books) are owned by your user:chown -R $USER:$USER ./booklore
- Ensure your local paths (e.g.,
Why This Setup Works
- Simplicity: Docker Compose handles networking, dependencies, and updates in one file.
- Security: Data is stored locally, not in the cloud.
- Portability: Move your library by migrating the
./bookloredirectory.
BookLore’s roadmap includes features like OPDS support and reading analytics. By self-hosting, you maintain full control over your digital library while enjoying a modern reading experience.
Pro tip:
Backup your docker-compose.yml and ./booklore directory regularly. To update, run docker-compose pull && docker-compose up -d.