Remote desktop access is essential for managing multiple Linux machines efficiently. Instead of physically moving between computers, you can remotely control them using the right tools. One of the best applications for this purpose is NoMachine, which offers seamless remote desktop functionality with minimal setup.
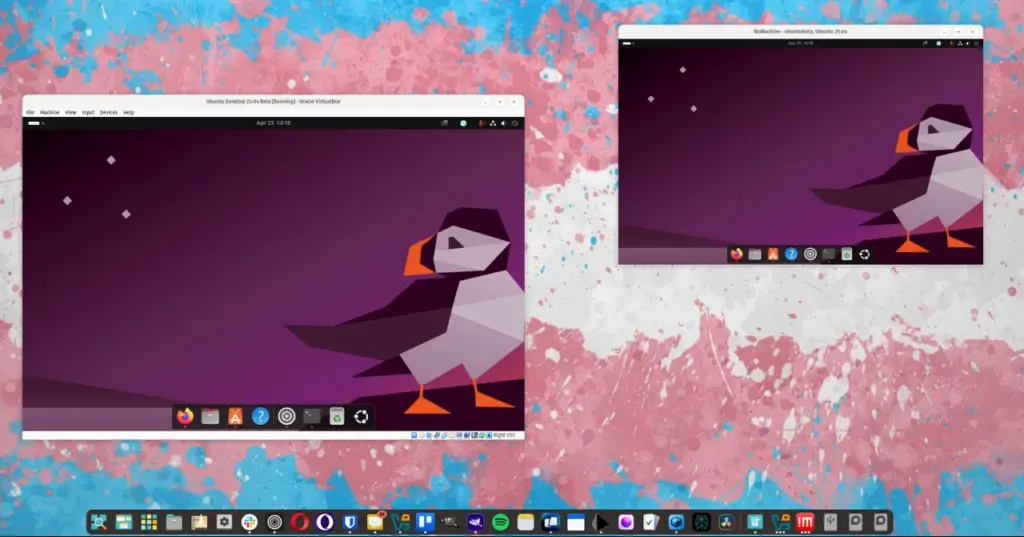
In this guide, I’ll walk you through installing and configuring NoMachine on Linux, ensuring secure and hassle-free remote connections.
Why Use NoMachine for Remote Access on Linux?
Setting up traditional RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) on Linux using tools like Xrdp can be complex, especially when dealing with different display servers (X.org, Wayland). NoMachine simplifies remote desktop access by:
- Working across different Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Fedora, etc.)
- Providing high-speed remote connections with minimal latency
- Supporting secure encrypted connections
- Offering an intuitive GUI for easy setup
Let’s dive into the installation and configuration process.
Prerequisites for Remote Desktop Setup
Before we begin, ensure you have:
- Two Linux machines (one as the remote host, the other as the client)
- A user account with sudo privileges on both systems
- A stable network connection (preferably LAN for best performance)
Step 1: Downloading and Installing NoMachine
1. Visit the NoMachine Download Page
Go to the NoMachine official download page and select the correct package for your distribution:
- DEB package (for Ubuntu, Debian, Pop!_OS)
- RPM package (for Fedora, CentOS, RHEL)
2. Install the Downloaded Package
On Debian/Ubuntu-based systems:
After downloading the .deb file, use:
sudo dpkg -i ~/Downloads/nomachine_*.debOn RPM-based systems (Fedora/RHEL):
Install the package using:
sudo rpm -i ~/Downloads/nomachine_*.rpmAfter installation, repeat the same steps on both machines—the remote host and the client.
Step 2: Configuring NoMachine on the Remote Computer
1. Start the NoMachine Service
On the remote machine, open the NoMachine Service application (usually found in your system menu).
Once opened, the service runs in the background, allowing incoming connections.
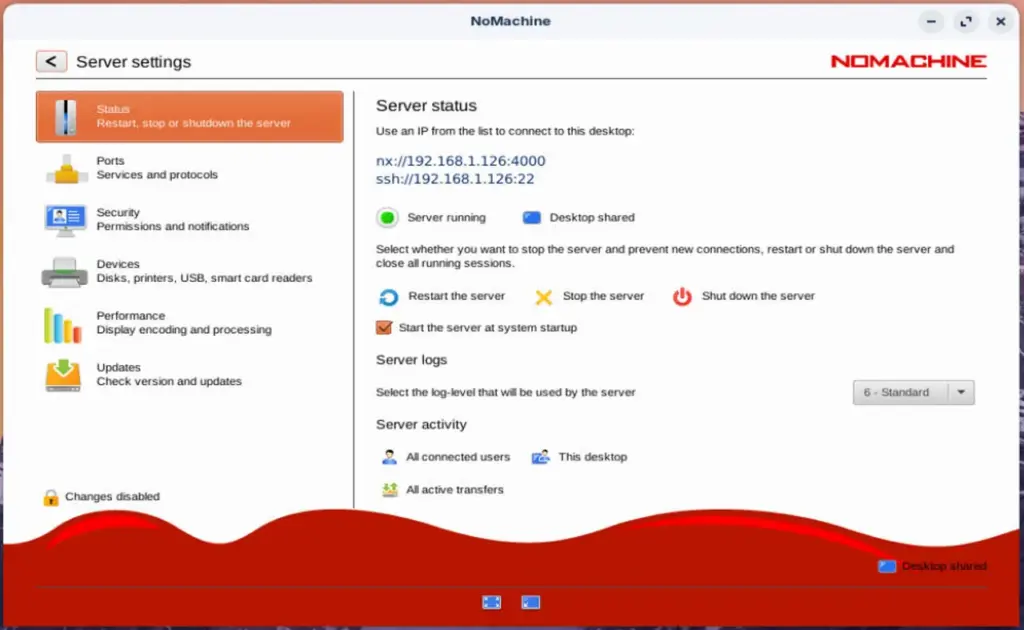
2. Adjust Settings (Optional)
If needed, tweak security and performance settings in the NoMachine Preferences panel, including:
- Session encryption level
- Authentication methods
- Session quality (balancing speed vs. quality)
But for most users, the default settings work perfectly.
Step 3: Connecting from the Local Machine
1. Launch NoMachine on the Client PC
Open the NoMachine application from your application menu. It will automatically scan the network for available machines.
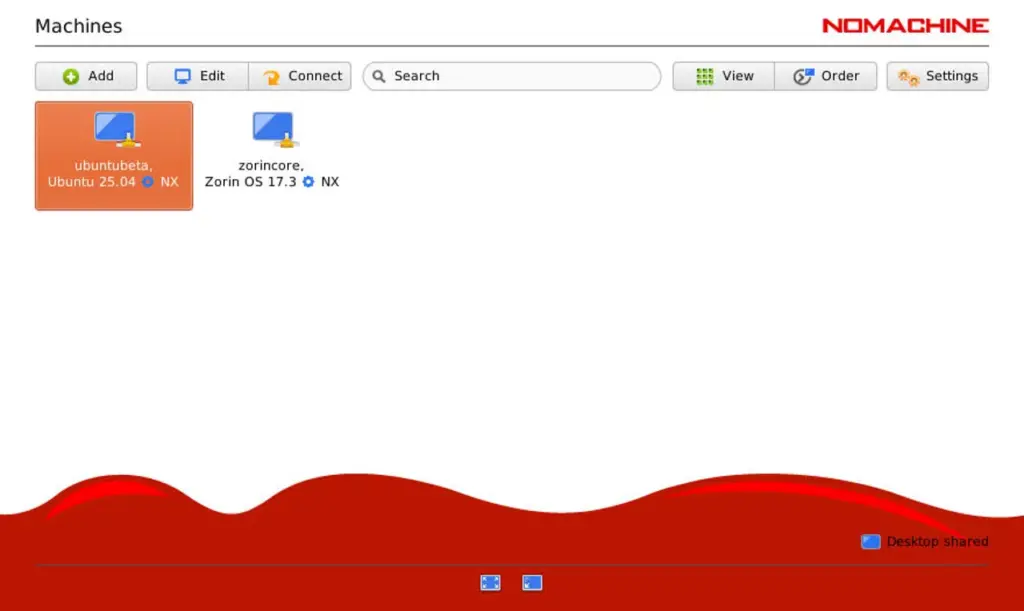
2. Establish the Connection
Double-click the detected remote machine, then:
- Verify the host fingerprint (click OK)
- Enter your remote Linux username & password
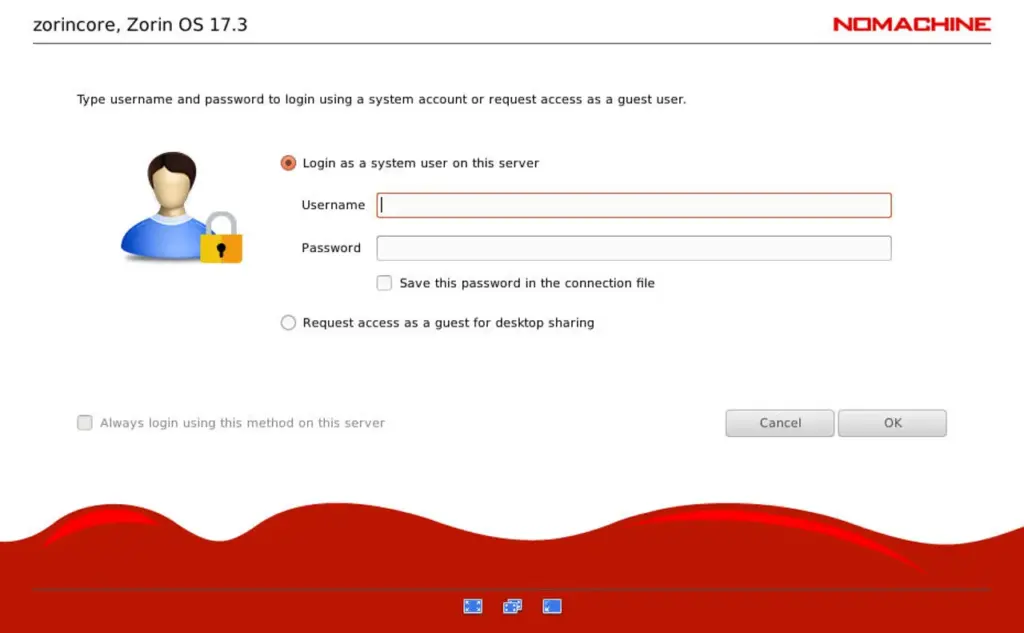
3. Complete Setup and Enjoy Remote Access
After authentication:
- A welcome wizard may appear—click through it.
- You now have full remote desktop control!
Troubleshooting Common Remote Desktop Issues
1. NoMachine Doesn’t Detect Remote Computers
- Ensure both machines are on the same network.
- Verify NoMachine service is running on the remote PC.
- Check local firewall settings (UFW/iptables may block connections).
2. Authentication Fails Even with Correct Credentials
- Try restarting the NoMachine service (
sudo service nomachine restart). - Reset the user password on the remote machine if necessary.
3. Lag or Poor Performance
- Lower graphics quality in NoMachine settings.
- Ensure a stable wired network connection (Wi-Fi can introduce latency).
Alternative Remote Desktop Tools for Linux
While NoMachine is excellent, other options include:
- X2Go – Lightweight, uses SSH for encryption.
- VNC (TigerVNC, RealVNC) – Simple but less secure without VPN.
- TeamViewer – Cross-platform but requires internet.
- AnyDesk – Fast, but proprietary with potential licensing costs.
NoMachine remains one of the best free, high-performance remote desktop solutions for Linux users.
Final Thoughts
Setting up remote desktop access on Linux with NoMachine is fast and hassle-free. With this guide, you can seamlessly control remote PCs as if you were sitting in front of them.
🚀 Start using NoMachine today and streamline your Linux workflow!