Key Takeaways
- Open-Source Milestone: A fully Apache 2.0 licensed model family that rivals proprietary giants like ElevenLabs and OpenAI.
- Ultra-Low Latency: Achieves first-packet latency of just 97ms, enabling genuine real-time conversational AI.
- Zero-Shot Capabilities: Clones voices from a 3-second audio sample or designs new voices from natural language descriptions.
- Multilingual Mastery: Supports 10 languages with state-of-the-art performance in cross-lingual synthesis.
Introduction: A Seismic Shift in Generative Voice AI
The text-to-speech (TTS) landscape has undergone a radical transformation. For years, enterprise-grade voice synthesis remained locked behind proprietary APIs and premium pricing models-ElevenLabs, Google Cloud TTS, and OpenAI’s audio preview dominated the market with closed-source models that demanded monthly subscriptions. Today, that monopoly is shattered. On January 21, 2026, Alibaba Cloud’s Qwen team released Qwen3-TTS, a fully open-source, Apache 2.0 licensed family of speech generation models that doesn’t just compete with commercial platforms-it surpasses them in critical performance metrics.
Qwen3-TTS represents the culmination of five years of speech synthesis research, trained on over 5 million hours of audio data spanning 10 languages. What makes this release genuinely paradigm-shifting isn’t merely the absence of licensing fees-it’s the technical breakthroughs embedded within: ultra-low latency voice generation, zero-shot voice cloning from just three seconds of audio, and natural language-driven voice design that transforms descriptive text into bespoke synthetic voices.
For developers, content creators, and AI enthusiasts in the addROM community, this is a watershed moment. You can now deploy enterprise-grade voice synthesis on your own infrastructure-whether that’s a Mac Mini M4, a Docker container, or a cloud server-without vendor lock-in or per-minute API costs.
Core Technical Breakthroughs: What Makes Qwen3-TTS Different
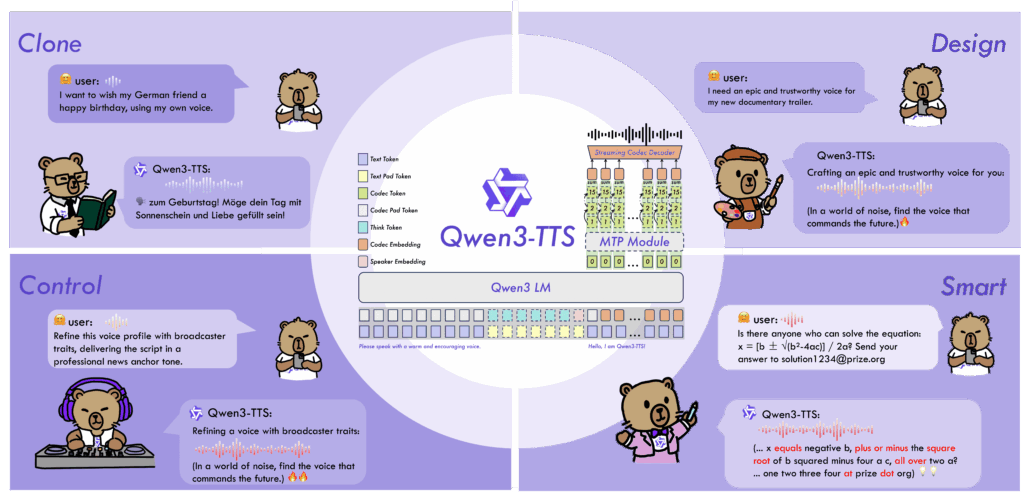
The Dual-Track Streaming Architecture
The Qwen3-TTS architecture eliminates traditional bottlenecks to achieve 97ms latency. Traditional TTS systems cascade through multiple stages: text-to-acoustic-features → language model → diffusion model → waveform generation. Each bottleneck introduces latency and potential information loss. Qwen3-TTS obliterates this pipeline.
Instead, the model adopts a discrete multi-codebook language model that handles the entire end-to-end speech generation process in a single forward pass. The result? A first-packet latency of just 97 milliseconds on the 0.6B variant and 101ms on the 1.7B model-meaning the model outputs the first frame of audio after receiving a single character of input. For real-time applications (conversational AI, live translation, interactive gaming), this latency profile is game-changing: it enables genuinely responsive dialogue without the awkward pauses that plague competing systems.
The Qwen3-TTS-Tokenizer-12Hz
Powering the low-latency generation is a self-developed speech tokenizer operating at 12Hz with 16 discrete codebooks. This multi-codebook approach is clever: the first layer encodes semantic content (what words are being said), while the remaining 15 layers capture fine-grained acoustic details-timbre, prosody, emotion, environmental characteristics. This hierarchical representation achieves extreme bitrate reduction while preserving paralinguistic information that makes voices sound genuinely human.
The 12Hz tokenizer enables streaming synthesis-the model can decode audio packets on-the-fly as text arrives, bit by bit. For contrast, the alternative 25Hz tokenizer prioritizes semantic richness and integrates with other Qwen audio models; developers can choose based on their use case.
Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) Module
Qwen3-TTS implements an innovative Multi-Token Prediction mechanism that predicts all 16 codebook layers from a single semantic input. This prevents the typical information bottleneck where acoustic details get lost during the transition from language modeling to audio reconstruction. The result is audio that preserves speaker identity, emotional nuance, and stylistic consistency even in long-form synthesis.
Key Features That Matter for Creators and Developers
1. Zero-Shot Voice Cloning in 3 Seconds
Provide a 3-second audio sample and the model extracts the speaker embedding instantly. The Qwen3-TTS base models (available in 0.6B and 1.7B parameter sizes) extract a speaker embedding and synthesize new speech in that voice without any fine-tuning. This capability extends across all 10 supported languages.
Practical implication: A YouTuber can clone their own voice for automated video narration. A game developer can create distinct NPC voices from sound effects. A accessibility advocate can preserve a family member’s voice for future communication devices.
On the Seed-TTS zero-shot cloning benchmark, Qwen3-TTS achieves a Word Error Rate (WER) of 1.24 on English-state-of-the-art compared to MiniMax, ElevenLabs, and commercial alternatives. Speaker similarity scores are highest across all 10 evaluated languages.
2. Voice Design: Create Voices from Text Descriptions
Unlike preset voice libraries, Qwen3-TTS allows you to synthesize entirely new voices from natural language descriptions. Describe a persona: “A warm, elderly British narrator with thoughtful pacing and gentle enthusiasm” or “An energetic Gen-Z streamer with high pitch and rapid speech patterns.” The model generates a fitting timbre and speaking style that matches your description.
This feature is powered by Qwen3’s underlying language model, which inherits robust text understanding capabilities. An optional “thinking pattern” was introduced during training to improve instruction-following for complex voice descriptions.
Implication: Game developers, animators, and narrative creators can design character voices on-demand without hiring voice talent. Animation studios can rapidly prototype dialogue deliveries before committing to professional recordings.
Pro Tip:
When designing voices, be specific about age, gender, accent, and speed. Adding descriptive adjectives regarding emotion (e.g., “melancholy,” “cheerful”) significantly improves the output consistency.
3. Expressive, Contextual Speech Synthesis
Qwen3-TTS doesn’t generate monotone audio; it adapts tone and rhythm based on context. The model demonstrates semantic-aware speech generation-it adapts tone, rhythm, pacing, and emotional expression based on the input text and optional natural language instructions.
Natural pausing is context-aware. Emphasis falls on important words. Complex information slows down; casual phrases accelerate. This results in remarkably human-like delivery for:
- Long-form content (audiobooks, podcasts, educational narrations)
- Multi-speaker conversations (dialogues, interviews, dramatizations)
- Instructional content (tutorials, documentation, guided meditations)
4. Robust Multilingual and Cross-Lingual Support
Qwen3-TTS covers 10 major languages: Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, German, French, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, and Italian-plus dialect variations (e.g., Sichuan Chinese, regional English accents).
More impressively: cross-lingual voice cloning. Clone a voice from a Chinese speaker and generate speech in that voice speaking English, German, or Japanese. This is crucial for international content distribution.
On the multilingual test set, Qwen3-TTS achieves the lowest average Word Error Rate in 6 of 10 languages and best speaker similarity across all 10 languages.
5. Streaming Output for Real-Time Applications
With 97ms first-packet latency and streaming architecture, Qwen3-TTS integrates seamlessly with LLM outputs. As a language model generates text token-by-token, Qwen3-TTS streams audio simultaneously-creating the illusion of a real-time conversational AI without awkward pauses. This is essential for:
- Conversational voice assistants
- Live translation and dubbing
- Real-time customer service bots
- Interactive gaming NPCs
Technical Specifications & Model Variants
| Model | Parameters | Key Capability | Streaming | Voice Control | Languages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-Base | 1.7B | 3-second voice cloning; fine-tuning ready | ✅ | Limited | 10 |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign | 1.7B | Custom voice creation from text descriptions | ✅ | (Natural Language) | 10 |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-CustomVoice | 1.7B | Style control over 9 premium pre-defined timbres | ✅ | (Instruction-based) | 10 |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-Base | 600M | Lightweight voice cloning; edge deployment | ✅ | Limited | 10 |
| Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-0.6B-CustomVoice | 600M | Efficient custom voice control for edge devices | ✅ | (Instruction-based) | 10 |
Model sizes: 2.5–4.5GB per model, enabling deployment on edge devices, Docker containers, or cloud servers.
Real-World Use Cases: From Content Creators to Accessibility
Content Creation & Short-Form Video
YouTubers and TikTok creators can leverage 49+ voice styles to produce professional narration without hiring voice actors. Qwen3-TTS maintains naturalness even at varied speaking speeds, making it ideal for:
- Product demonstrations and unboxing videos
- Educational content and tutorials
- Promotional clips and advertisements
- Audiobook production (with long-form stability)
The multilingual support makes global localization trivial-translate video scripts and generate narration in the local language while maintaining a consistent voice brand.
Accessibility & Assistive Technology
For users with speech disabilities or those using screen readers, Qwen3-TTS enables personalized, natural-sounding interfaces. A user can clone their own voice (or a family member’s) to create a persistent digital identity across applications.
Educational platforms can generate audio narration for textbooks, reducing production costs while making content accessible to visually impaired learners.
Gaming & Interactive Media
Game developers can create distinct NPC personas with different vocal characteristics-age, gender, accent, emotional tone-all synthesized on-the-fly. The emotional expressiveness means a character can sound angry, confused, or helpful depending on the dialogue context.
Enterprise Applications
- Virtual assistants operating at near-human conversational speed (97ms latency)
- Real-time customer service bots that sound genuinely empathetic
- Localization pipelines for global SaaS platforms
- Live translation with synchronized voice output
Performance Comparison: How Qwen3-TTS Stacks Up
| Metric | Qwen3-TTS | ElevenLabs | MiniMax-Speech | OpenAI GPT-4o Audio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Packet Latency | 97ms (0.6B) | 75–150ms | ~120ms | ~200ms+ |
| English WER (Seed-TTS) | 1.24% | ~2.5% | ~2.0% | ~2.5% |
| Speaker Similarity | Highest (All 10 langs) | Competitive | Competitive | Good |
| Streaming Support | Full streaming | Limited | Limited | (Preview only) |
| Voice Cloning Speed | 3-second sample | Requires fine-tuning | Limited | Not available |
| Voice Design (Natural Language) | Full support | Limited | No | Limited (GPT-4o-mini) |
| Open-Source / Self-Hosted | Apache 2.0 | Closed-source | Closed | Closed (API only) |
| Cost | Free (self-hosted) | ~$0.30/1M characters | Per-use API | ~$10/1M tokens |
Key Insight: Qwen3-TTS achieves state-of-the-art WER on the Seed-TTS benchmark while offering 3-second voice cloning and natural language voice design-features that remain either absent or limited in commercial competitors.
Why Open-Source Matters: The Democratization of Voice AI
Releasing Qwen3-TTS under the Apache 2.0 license is a statement: enterprise-grade voice synthesis should not require $5,000-$10,000+ annual API budgets. By open-sourcing both tokenizers and models, Alibaba has eliminated the technical and financial barriers that previously favored closed platforms.
Implications for the developer community:
- No vendor lock-in: Run models on your infrastructure, modify weights, fine-tune on custom data
- Privacy-first: Synthesize voices locally; no audio data leaves your servers
- Extreme cost reduction: Move from per-minute pricing to a one-time model download (~4GB)
- Research acceleration: Academic teams can build on state-of-the-art foundations
- Edge deployment: 0.6B models run efficiently on consumer hardware (Mac Mini M4, Raspberry Pi 5)
The addROM community of developers and content creators now has genuine alternatives to ElevenLabs and Google Cloud TTS-without sacrificing quality or paying per request.
Getting Started: Practical Integration
Qwen3-TTS models are available on Hugging Face and ModelScope (recommended for mainland China users). Download commands are straightforward:
# Via Hugging Face
huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign --local-dir ./Qwen3-TTS
# Via ModelScope (faster in China)
modelscope download --model Qwen/Qwen3-TTS-12Hz-1.7B-VoiceDesign --local_dir ./Qwen3-TTSQuick integration paths:
- Hugging Face Spaces: Interactive demos let you test VoiceDesign, CustomVoice, and standard TTS without local setup
- OpenAI-compatible FastAPI: Community implementations (GitHub) offer drop-in replacements for OpenAI TTS endpoints
- Docker containers: Pre-built images simplify local deployment
- vLLM integration: For high-throughput batch processing
Pro Tip:
For users in Mainland China or those experiencing slow speeds on Hugging Face, switch to ModelScope. The repository structure is identical, but download speeds are significantly optimized for Asian regions.
Limitations and Considerations
Where Qwen3-TTS excels: latency, voice cloning fidelity, multilingual expressiveness, and open-source accessibility.
Where it has room to grow:
- Chinese performance: CosyVoice 3 achieves slightly lower WER on Chinese-language tasks
- Setup complexity: Requires more configuration than cloud APIs (though community tools are simplifying this)
- Hardware requirements: Optimal performance requires GPU acceleration; CPU inference is slower
- Fine-tuning documentation: While fine-tuning is possible, official guides are still maturing
The Broader Implications: What This Means for 2026
The release of Qwen3-TTS signals a maturation of open-source voice AI. A year ago, commercial platforms had clear advantages; today, that gap has narrowed dramatically. For content creators, indie developers, and enterprises, this creates genuine competitive leverage in vendor negotiations and technical decisions.
In the addROM ecosystem-where self-hosted solutions, cost efficiency, and technical autonomy are core values-Qwen3-TTS represents exactly the kind of breakthrough that shifts the entire landscape. Voice cloning, voice design, and streaming audio synthesis are no longer exclusive features of premium commercial services.
Conclusion & Call to Action
Qwen3-TTS is a watershed moment for open-source voice AI. State-of-the-art zero-shot voice cloning, natural language voice design, ultra-low-latency streaming, multilingual support, and full self-hosting capability-at zero cost. For developers building voice assistants, content creators producing multilingual content, gaming studios designing character voices, and accessibility advocates creating inclusive interfaces, this release deserves serious evaluation.
Have you tested Qwen3-TTS yet? We’d love to hear about your use cases and benchmarks in the comments below. Are you exploring voice cloning for video automation? Using voice design to create game characters? Drop your experiments, findings, and integration strategies in the addROM community forum.
For deeper technical dives, check out the official Qwen3-TTS technical report on arXiv and join the conversation on GitHub and Hugging Face as this ecosystem evolves.
FAQ
Q: Can I use Qwen3-TTS for commercial projects?
A: Yes. Qwen3-TTS is released under the Apache 2.0 license, which allows for commercial use, modification, and distribution without requiring royalty fees.
Q: What hardware do I need to run the 1.7B model?
A: To run the 1.7B model efficiently with low latency, a GPU with at least 8GB VRAM (like an NVIDIA RTX 3060 or better) is recommended. For the 0.6B model, modern consumer CPUs or Apple Silicon (M-series) chips provide acceptable performance.
Q: Does Qwen3-TTS support languages other than the core 10?
A: Currently, the model is optimized for the 10 listed languages (English, Chinese, Japanese, etc.). While it may attempt other languages, performance will be significantly lower. However, the open-source nature means the community may fine-tune it for additional languages soon.
Q: How does the “Voice Design” feature differ from Voice Cloning?
A: Voice Cloning requires a reference audio file to mimic a specific person. Voice Design uses text prompts (e.g., “Deep, raspy male voice”) to generate a completely new, synthetic voice that doesn’t exist in the real world, which is ideal for creating unique characters.